**Community Solar Projects: How Neighborhoods are Going Green Together**
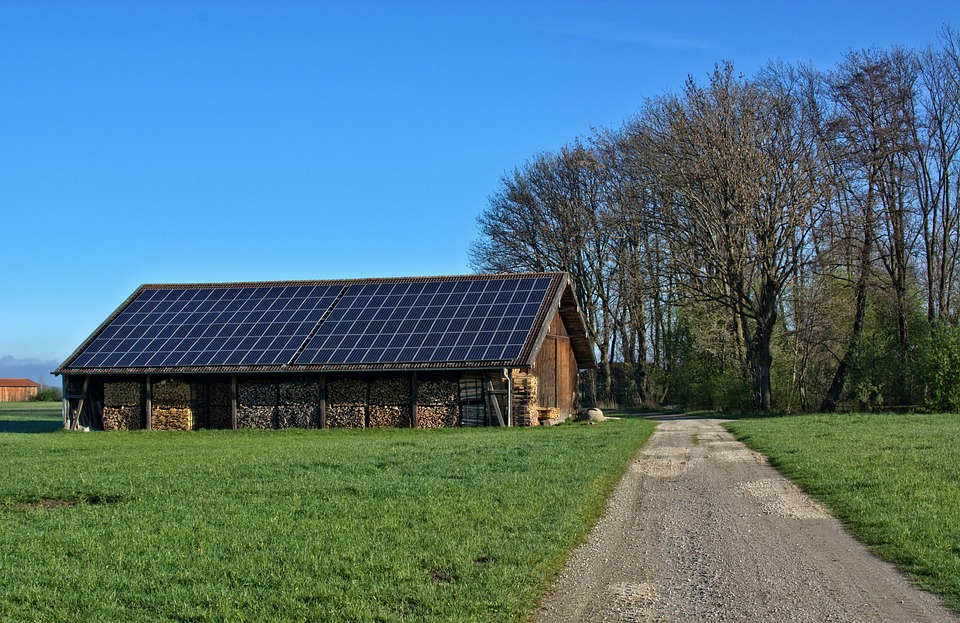
# Community Solar Projects: How Neighborhoods are Going Green Together It was one Saturday morning, the sun filtered through the leaves, creating a warm golden hue in our small community park. As I sipped my freshly brewed coffee from the local roastery, I couldn’t help but notice a buzz of excitement in the air. Neighbors gathered for a meeting, not just any ordinary gathering—this was about something revolutionary: Community Solar Projects. Their energy was palpable, electric even, as they discussed transforming their collective rooftops into a renewable energy powerhouse. It was a moment where community spirit met sustainable living, and I realized that going green with neighbors was becoming not only attainable but also enjoyable. ## What Are Community Solar Projects? Community solar projects are collaborative energy ventures where multiple households share the benefits of a large solar system, typically set up in a central location. Instead of installing solar panels on individual rooftops, participants invest in or rent a portion of a larger solar array. The electricity generated feeds into the local grid, and families receive credits on their utility bills based on their share of the power produced. This innovative solution empowers communities, making renewable energy accessible to everyone, regardless of property type or financial standing. ## Why Community Solar? ### 1. Accessibility for All Not everyone can install solar panels on their home. For renters, homeowners with shaded roofs, or those who can’t afford the upfront costs, community solar projects offer an alternative. By pooling resources, neighborhoods can harness the sun without the usual barriers, creating an inclusive environment. ### 2. Lower Costs Group purchasing power makes a significant difference. By participating in a community solar project, participants often enjoy lower costs compared to individual solar installations. Many projects come with financing options and incentives that further reduce expenses, facilitating a shift towards green energy for those who might find it financially daunting. ### 3. Environmental Impact Transitioning to solar energy significantly reduces reliance on fossil fuels, lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Community solar projects allow neighborhoods to contribute to a cleaner environment together, fostering a sense of shared responsibility and achievement. ### 4. Local Job Creation Community solar initiatives require a skilled workforce for installation, maintenance, and management. By investing in local solar projects, communities can stimulate job growth, directly benefitting their local economy while promoting sustainable practices. ### 5. Strengthening Community Ties What better way to bond with your neighbors than through a common goal? Community solar projects allow residents to work together, share knowledge, and celebrate milestones. From fundraising to installation day barbecues, every step in the process strengthens communal bonds. ## The Process: How to Start a Community Solar Project Starting a community solar project might sound intimidating, but it can be broken down into manageable steps. Here’s how neighborhoods can team up to make their solar dreams a reality: ### Step 1: Form a Solar Committee Gather interested neighbors and form a committee. This group will spearhead the project, organizing meetings, discussions, and outreach efforts. Having a dedicated team ensures that ideas are funneled into action. ### Step 2: Assess Community Interest Conduct surveys to gauge how many residents are interested in participating. Understanding the level of commitment will guide the project’s scale. Hold informational meetings to educate residents about the benefits of community solar. ### Step 3: Choose a Model There are various ownership models for community solar projects, including: – **Subscription model:** Subscribers pay for their share of the solar power generated. – **Equity model:** Participants invest capital, receiving returns based on the project’s revenue. – **Lease model:** A third party owns and operates the system, providing residents with the solar benefits without the hassle of management. Deciding on a model that fits the community’s needs is crucial. ### Step 4: Partner with Experts Engage with local solar developers or consultants to provide guidance and facilitate the project’s development. These professionals can help design the system, navigate regulations, and secure financing. ### Step 5: Site Selection Identify a suitable location for the solar array, considering factors like sun exposure, land ownership, and zoning regulations. Collaborate with local authorities to ensure compliance with local laws. ### Step 6: Fundraising Explore funding options, including grants, community crowdfunding, and local government incentives. Securing financial support is key to bringing the project to fruition. ### Step 7: Installation Work with a certified solar contractor to install the panels. This phase often involves community celebrations, such as a ground-breaking ceremony, emphasizing collective effort. ### Step 8: Monitor and Maintain Once the solar system is installed, ongoing maintenance is necessary for optimal energy production. Establish a monitoring system, and encourage community members to get involved in checking the performance of the solar array. ## Pro Tips for an Effective Community Solar Project 1. **Educate, Educate, Educate:** Prioritize information sessions to address concerns, myths, or misunderstandings about solar energy. Knowledge is power! 2. **Engage the Youth:** Involve schools and organizations like the Boy Scouts or Girl Scouts. Programs focused on sustainability can ignite young people’s interest, fostering their lifelong commitment to renewable energy. 3. **Start Small:** If the idea feels overwhelming, consider starting with a smaller pilot project before committing to a larger investment. This can help build momentum and offer valuable lessons. 4. **Celebrate Milestones:** Host social events to celebrate progress. From reaching fundraising goals to installation days, sharing successes fosters enthusiasm and camaraderie. 5. **Utilize Social Media:** Keep the community informed and engaged through social media updates, showcasing achievements and upcoming events. It’s a great way to keep the excitement alive! ## The Future of Community Solar Projects The future looks bright for community solar projects across the country. As more neighborhoods recognize the benefits of working together for sustainable energy, we can expect to see increased investments and innovative solutions. Government incentives are strengthening, making renewable energy more accessible than ever before. With supportive policies in many states and the growing need for renewable energy solutions, community solar projects are poised to become a